Maths-
General
Easy
Question
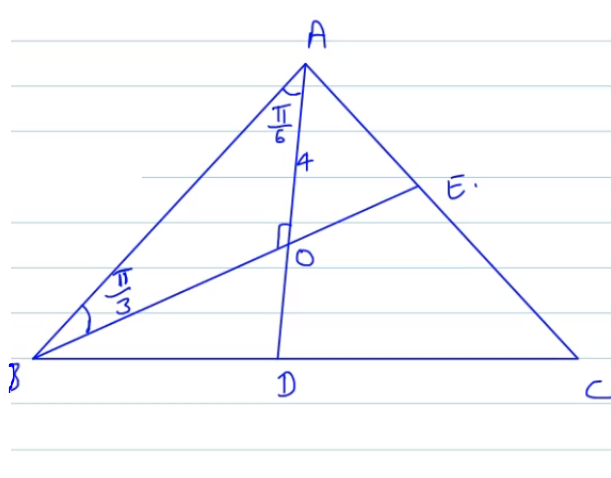
In triangle ABC, medians AD and BE are drawn. If AD=4, and
, then the area of the △ABC is

Every triangle has 3 medians, one from each vertex. AE, BF and CD are the 3 medians of the triangle ABC. The 3 medians always meet at a single point, no matter what the shape of the triangle is. The point where the 3 medians meet is called the centroid of the triangle.
The correct answer is: 
Given; AD=4, and BD=DC
Since the centroid O divides the line AD in the ratio 2:1
∴AO=
In △ABO,
In △ABO,



Related Questions to study
physics-
Two coherent sources S1 and S2 are separated by a distance four times the wavelength  of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
Two coherent sources S1 and S2 are separated by a distance four times the wavelength  of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
of the source. The sources lie along y axis whereas a detector moves along + x-axis. Leaving the origin and far off points the number of points where maxima are observed is
physics-General
physics-
Two coherent sources separated by distance d are radiating in phase having wavelength  . A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as
. A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as

Two coherent sources separated by distance d are radiating in phase having wavelength  . A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as
. A detector moves in a big circle around the two sources in the plane of the two sources. The angular position of n = 4 interference maxima is given as

physics-General
physics-
A beam with wavelength l falls on a stack of partially reflecting planes with separation d. The angle  that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)
that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)

A beam with wavelength l falls on a stack of partially reflecting planes with separation d. The angle  that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)
that the beam should make with the planes so that the beams reflected from successive planes may interfere constructively is (where n =1, 2, ……)

physics-General
physics-
Two ideal slits  and
and  are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength
are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength  passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through
passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through  as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is
as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is

Two ideal slits  and
and  are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength
are at a distance d apart and illuminated by light of wavelength  passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through
passing through an ideal source slit S placed on the line through  as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is
as shown. The distance between the planes of slits and the source slit is D. A screen is held at a distance D from the plane of the slits. The minimum value of d for which there is darkness at O is

physics-General
physics-
A monochromatic beam of light falls on YDSE apparatus at some angle (say  ) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit
) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit  . The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained
. The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained

A monochromatic beam of light falls on YDSE apparatus at some angle (say  ) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit
) as shown in figure. A thin sheet of glass is inserted in front of the lower slit  . The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained
. The central bright fringe (path difference = 0) will be obtained

physics-General
maths-
Find the sum of the infinite series 
Find the sum of the infinite series 
maths-General
physics-
In the figure is shown Young’s double slit experiment. Q is the position of the first bright fringe on the right side of O. P is the 11th fringe on the other side, as measured from Q. If the wavelength of the light used is  , then
, then  will be equal to
will be equal to

In the figure is shown Young’s double slit experiment. Q is the position of the first bright fringe on the right side of O. P is the 11th fringe on the other side, as measured from Q. If the wavelength of the light used is  , then
, then  will be equal to
will be equal to

physics-General
physics-
Figure here shows P and Q as two equally intense coherent sources emitting radiations of wavelength 20 m. The separation PQ is 5.0 m and phase of P is ahead of the phase of Q by  . A, B and C are three distant points of observation equidistant from the mid-point of PQ. The intensity of radiations at A, B, C will bear the ratio
. A, B and C are three distant points of observation equidistant from the mid-point of PQ. The intensity of radiations at A, B, C will bear the ratio

Figure here shows P and Q as two equally intense coherent sources emitting radiations of wavelength 20 m. The separation PQ is 5.0 m and phase of P is ahead of the phase of Q by  . A, B and C are three distant points of observation equidistant from the mid-point of PQ. The intensity of radiations at A, B, C will bear the ratio
. A, B and C are three distant points of observation equidistant from the mid-point of PQ. The intensity of radiations at A, B, C will bear the ratio

physics-General
physics-
In an interference arrangement similar to Young's double slit experiment, the slits  are illuminated with coherent microwave sources each of frequency
are illuminated with coherent microwave sources each of frequency  . The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by distance d = 150 m. The intensity I
. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by distance d = 150 m. The intensity I is measured as a function of
is measured as a function of  , where
, where  is defined as shown. If I0 is maximum intensity, then
is defined as shown. If I0 is maximum intensity, then  for
for  is given by
is given by

In an interference arrangement similar to Young's double slit experiment, the slits  are illuminated with coherent microwave sources each of frequency
are illuminated with coherent microwave sources each of frequency  . The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by distance d = 150 m. The intensity I
. The sources are synchronized to have zero phase difference. The slits are separated by distance d = 150 m. The intensity I is measured as a function of
is measured as a function of  , where
, where  is defined as shown. If I0 is maximum intensity, then
is defined as shown. If I0 is maximum intensity, then  for
for  is given by
is given by

physics-General
physics-
In the adjacent diagram, CP represents a wavefront and AO & BP, the corresponding two rays. Find the condition on  for constructive interference at P between the ray BP and reflected ray OP
for constructive interference at P between the ray BP and reflected ray OP

In the adjacent diagram, CP represents a wavefront and AO & BP, the corresponding two rays. Find the condition on  for constructive interference at P between the ray BP and reflected ray OP
for constructive interference at P between the ray BP and reflected ray OP

physics-General
physics-
A thin slice is cut out of a glass cylinder along a plane parallel to its axis. The slice is placed on a flat glass plate as shown. The observed interference fringes from this combination shall be

A thin slice is cut out of a glass cylinder along a plane parallel to its axis. The slice is placed on a flat glass plate as shown. The observed interference fringes from this combination shall be

physics-General
physics-
A ray of light of intensity I is incident on a parallel glass-slab at a point A as shown in fig. It undergoes partial reflection and refraction. At each reflection 25% of incident energy is reflected. The rays AB and AB undergo interference. The ratio  is
is

A ray of light of intensity I is incident on a parallel glass-slab at a point A as shown in fig. It undergoes partial reflection and refraction. At each reflection 25% of incident energy is reflected. The rays AB and AB undergo interference. The ratio  is
is

physics-General
maths-
If X and Y are two independent variables with means 5 and 10 and variances 4 and 9 respectively. If  , then r (U, V) is equal to-
, then r (U, V) is equal to-
If X and Y are two independent variables with means 5 and 10 and variances 4 and 9 respectively. If  , then r (U, V) is equal to-
, then r (U, V) is equal to-
maths-General
chemistry-
For the reaction If 1 mol of
,then the value of in the reaction is
For the reaction If 1 mol of
,then the value of in the reaction is
chemistry-General
physics-
Light wave is travelling along y-direction. If the corresponding  vector at any time is along the x-axis, the direction of
vector at any time is along the x-axis, the direction of  vector at that time is along
vector at that time is along

Light wave is travelling along y-direction. If the corresponding  vector at any time is along the x-axis, the direction of
vector at any time is along the x-axis, the direction of  vector at that time is along
vector at that time is along

physics-General



