Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A bob of mass  accelerates uniformly from rest to
accelerates uniformly from rest to  in time
in time  . As a function of
. As a function of  , the instantaneous power delivered to the body is
, the instantaneous power delivered to the body is

The correct answer is: 
From 

Velocity acquired in  sec
sec 
Power 
Related Questions to study
physics-
An aeroplane is flying in a horizontal direction with a velocity  at a height of 1960 m. when it is vertically above the point
at a height of 1960 m. when it is vertically above the point  on the ground, a body is dropped from it. The body strikes the ground at point
on the ground, a body is dropped from it. The body strikes the ground at point  . Calculate the distance
. Calculate the distance 
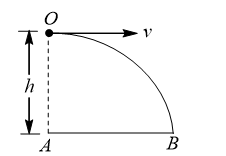
An aeroplane is flying in a horizontal direction with a velocity  at a height of 1960 m. when it is vertically above the point
at a height of 1960 m. when it is vertically above the point  on the ground, a body is dropped from it. The body strikes the ground at point
on the ground, a body is dropped from it. The body strikes the ground at point  . Calculate the distance
. Calculate the distance 

physics-General
Maths-
If the equation  represents an ellipse then
represents an ellipse then
If the equation  represents an ellipse then
represents an ellipse then
Maths-General
physics-
A particle of mass m moving with horizontal speed  as shown in figure. If
as shown in figure. If  than for one dimensional elastic collision, the speed of lighter particle after collision will be
than for one dimensional elastic collision, the speed of lighter particle after collision will be

A particle of mass m moving with horizontal speed  as shown in figure. If
as shown in figure. If  than for one dimensional elastic collision, the speed of lighter particle after collision will be
than for one dimensional elastic collision, the speed of lighter particle after collision will be

physics-General
Physics-
A particle of mass  attracted with a string of length
attracted with a string of length  is just revolving on the vertical circle without slacking of the string. If
is just revolving on the vertical circle without slacking of the string. If  and
and  are speed at position
are speed at position  and
and  then
then
A particle of mass  attracted with a string of length
attracted with a string of length  is just revolving on the vertical circle without slacking of the string. If
is just revolving on the vertical circle without slacking of the string. If  and
and  are speed at position
are speed at position  and
and  then
then

Physics-General
physics-
A simple pendulum is released from  as shown. If
as shown. If  and
and  represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum, the gain in kinetic energy at
represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum, the gain in kinetic energy at  is
is

A simple pendulum is released from  as shown. If
as shown. If  and
and  represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum, the gain in kinetic energy at
represent the mass of the bob and length of the pendulum, the gain in kinetic energy at  is
is

physics-General
Maths-
P(θ) and  are the pts. on the ellipse
are the pts. on the ellipse  then
then 
P(θ) and  are the pts. on the ellipse
are the pts. on the ellipse  then
then 
Maths-General
physics-
A ball of mass  rests on a vertical post of height
rests on a vertical post of height  . A bullet of mass
. A bullet of mass  , travelling with a velocity
, travelling with a velocity  in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of
in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of  and the bullet at a distance of
and the bullet at a distance of  from the foot of the post. The initial velocity
from the foot of the post. The initial velocity  of the bullet is
of the bullet is

A ball of mass  rests on a vertical post of height
rests on a vertical post of height  . A bullet of mass
. A bullet of mass  , travelling with a velocity
, travelling with a velocity  in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of
in a horizontal direction, hits the centre of the ball. After the collision, the ball and bullet travel independently. The ball hits the ground at a distance of  and the bullet at a distance of
and the bullet at a distance of  from the foot of the post. The initial velocity
from the foot of the post. The initial velocity  of the bullet is
of the bullet is

physics-General
physics-
A particle  is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl. It passes the point
is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl. It passes the point  at
at  . At this instant of time, the horizontal component of its velocity
. At this instant of time, the horizontal component of its velocity  . A bead
. A bead  of the same mass as
of the same mass as  is ejected from
is ejected from  to
to  along the horizontal string
along the horizontal string  (see figure) with the speed
(see figure) with the speed  . Friction between the bead and the string may be neglected. Let
. Friction between the bead and the string may be neglected. Let  and
and  be the respective time taken by
be the respective time taken by  and
and  to reach the point
to reach the point  . Then
. Then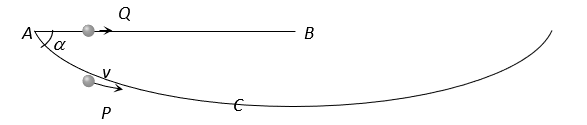
A particle  is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl. It passes the point
is sliding down a frictionless hemispherical bowl. It passes the point  at
at  . At this instant of time, the horizontal component of its velocity
. At this instant of time, the horizontal component of its velocity  . A bead
. A bead  of the same mass as
of the same mass as  is ejected from
is ejected from  to
to  along the horizontal string
along the horizontal string  (see figure) with the speed
(see figure) with the speed  . Friction between the bead and the string may be neglected. Let
. Friction between the bead and the string may be neglected. Let  and
and  be the respective time taken by
be the respective time taken by  and
and  to reach the point
to reach the point  . Then
. Then
physics-General
Maths-
If the chords of contact of  and
and  w.r.t the ellipse
w.r.t the ellipse  are at right angle then
are at right angle then 
If the chords of contact of  and
and  w.r.t the ellipse
w.r.t the ellipse  are at right angle then
are at right angle then 
Maths-General
Maths-
The area of an ellipse is 8π sq. units dist. between the foci is  then e=
then e=
The area of an ellipse is 8π sq. units dist. between the foci is  then e=
then e=
Maths-General
Physics-
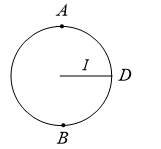
A point  moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of
moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of  is such that it sweeps out a length
is such that it sweeps out a length  , where
, where  is in metres and
is in metres and  is in seconds. The radius of the path is
is in seconds. The radius of the path is  . The acceleration of
. The acceleration of  when
when  is nearly
is nearly

A point  moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of
moves in counter-clockwise direction on a circular path as shown in the figure. The movement of  is such that it sweeps out a length
is such that it sweeps out a length  , where
, where  is in metres and
is in metres and  is in seconds. The radius of the path is
is in seconds. The radius of the path is  . The acceleration of
. The acceleration of  when
when  is nearly
is nearly

Physics-General
physics-
In a two dimensional motion of a particle, the particle moves from point  , position vector
, position vector  . If the magnitudes of these vectors are respectively,
. If the magnitudes of these vectors are respectively,  =3 and
=3 and  and the angles they make with the
and the angles they make with the  -axis are
-axis are  and 15
and 15 , respectively, then find the magnitude of the displacement vector
, respectively, then find the magnitude of the displacement vector
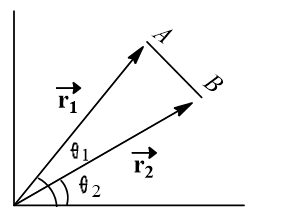
In a two dimensional motion of a particle, the particle moves from point  , position vector
, position vector  . If the magnitudes of these vectors are respectively,
. If the magnitudes of these vectors are respectively,  =3 and
=3 and  and the angles they make with the
and the angles they make with the  -axis are
-axis are  and 15
and 15 , respectively, then find the magnitude of the displacement vector
, respectively, then find the magnitude of the displacement vector

physics-General
physics-
A block(B) is attached to two unstretched springs  with springs constants
with springs constants  representively (see Fig. I) The other ends are attached to identical supports
representively (see Fig. I) The other ends are attached to identical supports  and
and  not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block
not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block  is displaced towards wall I by small distance
is displaced towards wall I by small distance  and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2.Displacements
and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2.Displacements  are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block
are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block  The ratio
The ratio  is
is

A block(B) is attached to two unstretched springs  with springs constants
with springs constants  representively (see Fig. I) The other ends are attached to identical supports
representively (see Fig. I) The other ends are attached to identical supports  and
and  not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block
not attached to the walls. The springs and supports have negligible mass. There is no friction anywhere. The block  is displaced towards wall I by small distance
is displaced towards wall I by small distance  and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2.Displacements
and released. The block returns and moves a maximum distance y towards wall 2.Displacements  are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block
are measured with respect to the equilibrium position of the block  The ratio
The ratio  is
is

physics-General
physics-
A small roller coaster starts at point A with a speed  on a curved track as shown in the figure.
on a curved track as shown in the figure.
The friction between the roller coaster and the track is negligible and it always remains in contact with the track. The speed of roller coaster at point  on the track will be
on the track will be

A small roller coaster starts at point A with a speed  on a curved track as shown in the figure.
on a curved track as shown in the figure.
The friction between the roller coaster and the track is negligible and it always remains in contact with the track. The speed of roller coaster at point  on the track will be
on the track will be

physics-General
Physics-
A body of mass  is moving with a uniform speed
is moving with a uniform speed  along a circle of radius
along a circle of radius  , what is the average acceleration in going from
, what is the average acceleration in going from  to
to  ?
?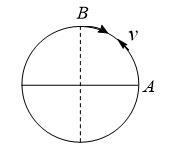
A body of mass  is moving with a uniform speed
is moving with a uniform speed  along a circle of radius
along a circle of radius  , what is the average acceleration in going from
, what is the average acceleration in going from  to
to  ?
?
Physics-General



