Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A small body of mass  slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius
slides down from the top of a hemisphere of radius  . The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is
. The surface of block and hemisphere are frictionless. The height at which the body lose contact with the surface of the sphere is

The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
Physics-
The trajectory of a particle moving in vast maidan is as shown in the figure. The coordinates of a position  are
are  The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
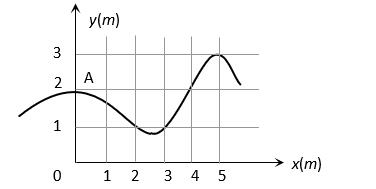
The trajectory of a particle moving in vast maidan is as shown in the figure. The coordinates of a position  are
are  The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are
The coordinates of another point at which the instantaneous velocity is same as the average velocity between the points are

Physics-General
physics-
A point mass  is suspended from a light thread of length
is suspended from a light thread of length  fixed at
fixed at , is whirled in a horizontal circle at constant speed as shown. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, the forces on the mass are
, is whirled in a horizontal circle at constant speed as shown. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, the forces on the mass are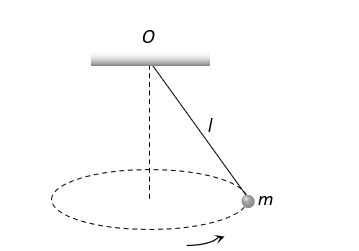
A point mass  is suspended from a light thread of length
is suspended from a light thread of length  fixed at
fixed at , is whirled in a horizontal circle at constant speed as shown. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, the forces on the mass are
, is whirled in a horizontal circle at constant speed as shown. From your point of view, stationary with respect to the mass, the forces on the mass are
physics-General
physics-
A particle is projected from a point  with velocity
with velocity  at an angle of
at an angle of  with horizontal as shown in figure. It strikes the plane
with horizontal as shown in figure. It strikes the plane  at right angles. The velocity of the particle at the time of collision is
at right angles. The velocity of the particle at the time of collision is

A particle is projected from a point  with velocity
with velocity  at an angle of
at an angle of  with horizontal as shown in figure. It strikes the plane
with horizontal as shown in figure. It strikes the plane  at right angles. The velocity of the particle at the time of collision is
at right angles. The velocity of the particle at the time of collision is

physics-General
chemistry-
Assertion: At constant pressure for the change H2O(s)→H2O(g) work done is negative.
Reason: During phase transition work done is always negative.
Assertion: At constant pressure for the change H2O(s)→H2O(g) work done is negative.
Reason: During phase transition work done is always negative.
chemistry-General
chemistry-
In view of the signs of DG° or the following reactions:
PbO2 +Pb→2PbO,DrG°<0
SnO2 +Sn→2SnO,DrG°>0, which oxidation states are more characteristic for lead and tin?
In view of the signs of DG° or the following reactions:
PbO2 +Pb→2PbO,DrG°<0
SnO2 +Sn→2SnO,DrG°>0, which oxidation states are more characteristic for lead and tin?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Considerthereaction:4NO2(g) O2(g) →2N2O5(g) ,DH=–111kJ IfN2O5(s)isformedinsteadofN2O5(g)intheabove reaction,theDHvaluewillbe:(given,DHofsublimationfor N2O5is54kJmol )</span
Considerthereaction:4NO2(g) O2(g) →2N2O5(g) ,DH=–111kJ IfN2O5(s)isformedinsteadofN2O5(g)intheabove reaction,theDHvaluewillbe:(given,DHofsublimationfor N2O5is54kJmol )</span
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Thevalueofenthalpychange(DH)forthe reactionC2H5OH(l)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+3H2O(l) at 27°Cis–1366.5kJmol–1.The valueofinter- nalenergychangefortheabovereactionat this temperaturewillbe-
Thevalueofenthalpychange(DH)forthe reactionC2H5OH(l)+3O2(g)→2CO2(g)+3H2O(l) at 27°Cis–1366.5kJmol–1.The valueofinter- nalenergychangefortheabovereactionat this temperaturewillbe-
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Fromthethermochemicalreactions,C(graphite)+½O2 →CO;DH=–110.5KJ CO+1/2O2 →CO2;DH=–83.2KJ Theheatofreactionof C(graphite)+O2 →CO2is-
Fromthethermochemicalreactions,C(graphite)+½O2 →CO;DH=–110.5KJ CO+1/2O2 →CO2;DH=–83.2KJ Theheatofreactionof C(graphite)+O2 →CO2is-
chemistry-General
chemistry-
TheDH° for CO2(g) ,CO(g) and H2O(g) are –393.5,–110.5and–241.8Kjmol–1respectively the standard enthalpychange (in KJ) for the reactionCO2(g)+H2(g)→CO(g)+H2O(g)is-
TheDH° for CO2(g) ,CO(g) and H2O(g) are –393.5,–110.5and–241.8Kjmol–1respectively the standard enthalpychange (in KJ) for the reactionCO2(g)+H2(g)→CO(g)+H2O(g)is-
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Which of the followingequationsrespresents standardheatofformationofCH4 ?
Which of the followingequationsrespresents standardheatofformationofCH4 ?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
2molesof COaremixedwith 1moleofO2ina containerof1l.Theycompletelytoform2moles ofCO2.Ifthe pressurein the vesselchanges from70atmto40atm,whatwill bethevalue of DU in kJat500K(The gasesdeviateappreciably from idealbehaviour.) 2CO+O2→2CO2;DH=-560kJ/mol, 1Latm=0.1kJ For theprocessH2O(l)(1 bar,373K)→H2O(g) (1bar,373K),thecorrect setofthermodynamic parametersis-
2molesof COaremixedwith 1moleofO2ina containerof1l.Theycompletelytoform2moles ofCO2.Ifthe pressurein the vesselchanges from70atmto40atm,whatwill bethevalue of DU in kJat500K(The gasesdeviateappreciably from idealbehaviour.) 2CO+O2→2CO2;DH=-560kJ/mol, 1Latm=0.1kJ For theprocessH2O(l)(1 bar,373K)→H2O(g) (1bar,373K),thecorrect setofthermodynamic parametersis-
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The conversion A to B is carried out by the following path:
Given: DS(A→C) =50e.u.,DS(C→D) =30 e.u., DS(B→D) =20e.u. Where e.u.is entropy unit then DS(A→B) is
The conversion A to B is carried out by the following path:
Given: DS(A→C) =50e.u.,DS(C→D) =30 e.u., DS(B→D) =20e.u. Where e.u.is entropy unit then DS(A→B) is
chemistry-General
physics-
Three balls are dropped from the top of a building with equal speed at different angles. When the balls strike ground their velocities are  and
and  respectively, then
respectively, then

Three balls are dropped from the top of a building with equal speed at different angles. When the balls strike ground their velocities are  and
and  respectively, then
respectively, then

physics-General
Maths-
When does the current flow through the following circuit ?

When does the current flow through the following circuit ?

Maths-General
Maths-
The following circuit when expressed in symbolic form of logic is :

The following circuit when expressed in symbolic form of logic is :

Maths-General



