Question
A square loop of side 5 cm enters a magnetic field with 1 cms-1. The front edge enters the magnetic field at t = 0 then which graph best depicts emf

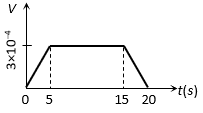
The correct answer is: 
When loop is entering in the field, magnetic flux (i.e. ´) linked with the loop increases so induced emf in it  =
= (Negative) .
(Negative) .
When loop completely entered in the field (after 5 sec) flux linked with the loop remains constant so e = 0.
After 15 sec, loop begins to exit out, linked magnetic flux decreases so induced emf  (Positive)
(Positive)
Related Questions to study
Switch S of the circuit shown in figure. is closed at t = 0. If e denotes the induced

emf in L and i, the current flowing through the circuit at time t, which of the following graphs is correct
Switch S of the circuit shown in figure. is closed at t = 0. If e denotes the induced

emf in L and i, the current flowing through the circuit at time t, which of the following graphs is correct
The current i in an induction coil varies with time t according to the graph shown

in figure. Which of the following graphs shows the induced emf (e) in the coil with time
The current i in an induction coil varies with time t according to the graph shown

in figure. Which of the following graphs shows the induced emf (e) in the coil with time
A flexible wire bent in the form of a circle is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The radius of the coil changes as shown in figure. The graph of induced emf in the coil is represented by

A flexible wire bent in the form of a circle is placed in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to the plane of the coil. The radius of the coil changes as shown in figure. The graph of induced emf in the coil is represented by

When a certain circuit consisting of a constant e.m.f. E an inductance L and a resistance R is closed, the current in, it increases with time according to curve 1. After one parameter (E, L or R) is changed, the increase in current follows curve 2 when the circuit is closed second time. Which parameter was changed and in what direction

When a certain circuit consisting of a constant e.m.f. E an inductance L and a resistance R is closed, the current in, it increases with time according to curve 1. After one parameter (E, L or R) is changed, the increase in current follows curve 2 when the circuit is closed second time. Which parameter was changed and in what direction

In the following figure, the magnet is moved towards the coil with a speed v and induced emf is e. If magnet and coil recede away from one another each moving with speed v, the induced emf in the coil will be

In the following figure, the magnet is moved towards the coil with a speed v and induced emf is e. If magnet and coil recede away from one another each moving with speed v, the induced emf in the coil will be

The equation  . where a, b, c are the sides of a ΔABC, and the equation
. where a, b, c are the sides of a ΔABC, and the equation  have a common root. The measure of
have a common root. The measure of  is-
is-
in a right angled isosceles triangle, ratio of sides = 1:√2:1
base angles are = 45 degrees.
The equation  . where a, b, c are the sides of a ΔABC, and the equation
. where a, b, c are the sides of a ΔABC, and the equation  have a common root. The measure of
have a common root. The measure of  is-
is-
in a right angled isosceles triangle, ratio of sides = 1:√2:1
base angles are = 45 degrees.
If in a ΔABC, (sin A + sin B + sin C)(sin A + sin B – sin C)= 3 sin A sin B, then –
the sine rule states that
a/sin A =b/sin B = c/sinC = 2R
this is used to find the relation of the angles and sides of the triangles.
If in a ΔABC, (sin A + sin B + sin C)(sin A + sin B – sin C)= 3 sin A sin B, then –
the sine rule states that
a/sin A =b/sin B = c/sinC = 2R
this is used to find the relation of the angles and sides of the triangles.
In the adjacent figure 'P' is any interior point of the equilateral triangle ABC of side length 2 unit –

If xa, xb and xc represent the distance of P from the sides BC, CA and AB respectively then xa + xb + xc is equal to -
area of equilateral triangle = √3a2/4
area of triangle = 1/2 x base x height
In the adjacent figure 'P' is any interior point of the equilateral triangle ABC of side length 2 unit –

If xa, xb and xc represent the distance of P from the sides BC, CA and AB respectively then xa + xb + xc is equal to -
area of equilateral triangle = √3a2/4
area of triangle = 1/2 x base x height
The expression  is equal to -
is equal to -
In a triangle ABC, cos A = (b2+c2-a2)/2bc
The expression  is equal to -
is equal to -
In a triangle ABC, cos A = (b2+c2-a2)/2bc
In the figure, if AB = AC,  and AE = AD, then x is equal to
and AE = AD, then x is equal to

exterior angle = sum of interior opposite angles is a property of triangles
sum of interior angles of a triangle = 180 degree
In the figure, if AB = AC,  and AE = AD, then x is equal to
and AE = AD, then x is equal to

exterior angle = sum of interior opposite angles is a property of triangles
sum of interior angles of a triangle = 180 degree
Statement- (1) : The tangents drawn to the parabola y2 = 4ax at the ends of any focal chord intersect on the directrix.
Statement- (2) : The point of intersection of the tangents at drawn at P(t1) and Q(t2) are the parabola y2 = 4ax is {at1t2, a(t1 + t2)}
Statement- (1) : The tangents drawn to the parabola y2 = 4ax at the ends of any focal chord intersect on the directrix.
Statement- (2) : The point of intersection of the tangents at drawn at P(t1) and Q(t2) are the parabola y2 = 4ax is {at1t2, a(t1 + t2)}
Statement- (1) : PQ is a focal chord of a parabola. Then the tangent at P to the parabola is parallel to the normal at Q.
Statement- (2) : If P(t1) and Q(t2) are the ends of a focal chord of the parabola y2 = 4ax, then t1t2 = –1.
slopes at the two extremeties of a focal chord are : (t,-1/t)
this property is used to explain the behaviour of tangents and normals at the respective points.
Statement- (1) : PQ is a focal chord of a parabola. Then the tangent at P to the parabola is parallel to the normal at Q.
Statement- (2) : If P(t1) and Q(t2) are the ends of a focal chord of the parabola y2 = 4ax, then t1t2 = –1.
slopes at the two extremeties of a focal chord are : (t,-1/t)
this property is used to explain the behaviour of tangents and normals at the respective points.



