Question
In case of nitrogen, is possible but not
while in case of phosphorus,
as well
as are possible. It is due to
Lower electronegativity of P but not in N
Lower tendency of H bond formation in P than N
Availability of vacant -orbital in P but not in N
Occurrence of P in solid while N in gaseous state at room temperature
Lower electronegativity of P but not in N
Lower tendency of H bond formation in P than N
Availability of vacant -orbital in P but not in N
Occurrence of P in solid while N in gaseous state at room temperature
The correct answer is: Availability of vacant -orbital in P but not in N
Nitrogen does not have -orbitals
Related Questions to study
A hollow charged metal sphere has radius r . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance 3r from the centre is V, then electric field intensity at a distance 3r is
A hollow charged metal sphere has radius r . If the potential difference between its surface and a point at a distance 3r from the centre is V, then electric field intensity at a distance 3r is
Two spheres of radii and
joined by a fine wire are raised to a potential V. Let the surface charge densities at these two spheres be
and
respectively. Then the ratio
has a value
Two spheres of radii and
joined by a fine wire are raised to a potential V. Let the surface charge densities at these two spheres be
and
respectively. Then the ratio
has a value
A large insulated sphere of radius r charged with Q units of electricity is placed in contact with a small insulated uncharged sphere of radius r and in then separated. The charge on smaller sphere will now be
A large insulated sphere of radius r charged with Q units of electricity is placed in contact with a small insulated uncharged sphere of radius r and in then separated. The charge on smaller sphere will now be
The magnitude of electric field in the annual region of a charged cylindrical capacitor
The magnitude of electric field in the annual region of a charged cylindrical capacitor
The equivalent capacitance across  Fig is
Fig is
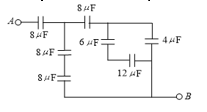
The equivalent capacitance across  Fig is
Fig is

What is the potential difference across 2 F capacitor in the circuit shown?
F capacitor in the circuit shown?

What is the potential difference across 2 F capacitor in the circuit shown?
F capacitor in the circuit shown?

The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge q and radius R will be
The maximum field intensity on the axis of a uniformly charged ring of charge q and radius R will be



