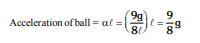Science
Ingestion-and-Digestion-1
Easy
Question
A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length  is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude
is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude  The rod is released from shown position from rest.
The rod is released from shown position from rest.
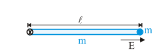
What is the acceleration of the small ball at the instant of releasing the rod?
The correct answer is: 
Related Questions to study
science
A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length  is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude
is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude  The rod is released from shown position from rest.
The rod is released from shown position from rest.
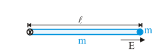
What is the angular acceleration of the rod at the instant of releasing the rod?
A thin homogeneous rod of mass m and length  is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude
is free to rotate in vertical plane about a horizontal axle pivoted at one end of the rod. A small ball of mass m and charge q is attached to the opposite end of this rod. The whole system is positioned in a constant horizontal electric field of magnitude  The rod is released from shown position from rest.
The rod is released from shown position from rest.

What is the angular acceleration of the rod at the instant of releasing the rod?
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
Consider a finite charged rod. Electric field at Point P (shown) makes an angle  with horizontal dotted line then angle
with horizontal dotted line then angle  is :-
is :-
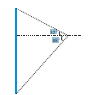
Consider a finite charged rod. Electric field at Point P (shown) makes an angle  with horizontal dotted line then angle
with horizontal dotted line then angle  is :-
is :-
 scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
The diagram shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius R. It has volume charge density  . If the electric field at a point 2R distance above its centre is E then what is the electric field at the point which is 2R below its centre?
. If the electric field at a point 2R distance above its centre is E then what is the electric field at the point which is 2R below its centre?
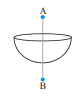
The diagram shows a uniformly charged hemisphere of radius R. It has volume charge density  . If the electric field at a point 2R distance above its centre is E then what is the electric field at the point which is 2R below its centre?
. If the electric field at a point 2R distance above its centre is E then what is the electric field at the point which is 2R below its centre?
 scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
A metallic rod of length l rotates at angular velocity  about an axis passing through one end and perpendiuclar to the rod. If mass of electron is m and its charge is –e then the magnitude of potential difference between its two ends is
about an axis passing through one end and perpendiuclar to the rod. If mass of electron is m and its charge is –e then the magnitude of potential difference between its two ends is
A metallic rod of length l rotates at angular velocity  about an axis passing through one end and perpendiuclar to the rod. If mass of electron is m and its charge is –e then the magnitude of potential difference between its two ends is
about an axis passing through one end and perpendiuclar to the rod. If mass of electron is m and its charge is –e then the magnitude of potential difference between its two ends is
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
Uniform electric field of magnitude 100 V/m in space is directed along the line  . Find the potential difference between point A (3, 1) & B (1,3).
. Find the potential difference between point A (3, 1) & B (1,3).
Uniform electric field of magnitude 100 V/m in space is directed along the line  . Find the potential difference between point A (3, 1) & B (1,3).
. Find the potential difference between point A (3, 1) & B (1,3).
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
A small electric dipole is placed at origin with its dipole moment directed along positive x-axis. The direction of electric field at point  is
is
A small electric dipole is placed at origin with its dipole moment directed along positive x-axis. The direction of electric field at point  is
is
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
Four charges are placed at the circumference of a dial clock as shown in figure If the clock has only hour hand, then the resultant force on a charge  placed at the centre, points in the direction which shows the time as :–
placed at the centre, points in the direction which shows the time as :–
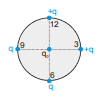
Four charges are placed at the circumference of a dial clock as shown in figure If the clock has only hour hand, then the resultant force on a charge  placed at the centre, points in the direction which shows the time as :–
placed at the centre, points in the direction which shows the time as :–
 scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
For a spherically symmetrical charge distribution, electric field at a distance r from the centre of sphere is  where k is a constant. What will be the volume charge density at a distance r from the centre of sphere ?
where k is a constant. What will be the volume charge density at a distance r from the centre of sphere ?
For a spherically symmetrical charge distribution, electric field at a distance r from the centre of sphere is  where k is a constant. What will be the volume charge density at a distance r from the centre of sphere ?
where k is a constant. What will be the volume charge density at a distance r from the centre of sphere ?
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
Two positrons (e+) and two protons (P) are kept on four corners of a square of side a as shown in figure. The mass of proton is much larger than the mass of positron. Let q denotes the charge on the proton as well as the positron then the kinetic energies of one of the positrons and one of the protons respectively after a very long time will be
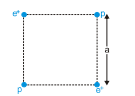
Two positrons (e+) and two protons (P) are kept on four corners of a square of side a as shown in figure. The mass of proton is much larger than the mass of positron. Let q denotes the charge on the proton as well as the positron then the kinetic energies of one of the positrons and one of the protons respectively after a very long time will be
 scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
scienceingestion-and-digestion-1
science
The air above the ocean and lakes is dry.
The air above the ocean and lakes is dry.
scienceGrade-4-
science
The amount of water vapor in the air is calculated as humidity.
The amount of water vapor in the air is calculated as humidity.
scienceGrade-4-
science
The amount of rainfall is measured by using a hygrometer.
The amount of rainfall is measured by using a hygrometer.
scienceGrade-4-
science
The humidity in deserts is typically very low.
The humidity in deserts is typically very low.
scienceGrade-4-
science
It is not easy to walk against the wind on a windy day.
It is not easy to walk against the wind on a windy day.
scienceGrade-4-
science
Jasmine carried out an experiment. She placed two bowls of sand and water in the sunlight. She took the temperatures after an hour. She then took both the bowls into her home and placed them in an area with no light. She took another temperature after an hour and conducted the following observations:
| Sand |
Water |
|
| Before placing the bowls in the sunlight |
370C |
300C |
| After keeping the bowls in the sunlight for one hour |
370C |
320C |
| After keeping the bowl inside the house for one hour |
310C |
310C |
Jasmine carried out an experiment. She placed two bowls of sand and water in the sunlight. She took the temperatures after an hour. She then took both the bowls into her home and placed them in an area with no light. She took another temperature after an hour and conducted the following observations:
| Sand |
Water |
|
| Before placing the bowls in the sunlight |
370C |
300C |
| After keeping the bowls in the sunlight for one hour |
370C |
320C |
| After keeping the bowl inside the house for one hour |
310C |
310C |
scienceGrade-4-