Maths-
General
Easy
Question
The converse of “if in a triangle ABC, AB =AC then  is
is
- If in a triangle

- If in a triangle

- If in a triangle

- If in a triangle


Let p -> q is the relation. Then, the converse of the relation becomes q -> p.
The correct answer is: If in a triangle 
Given That:
The converse of “if in a triangle ABC, AB =AC then  is
is
>>> Let p -> q is the relation. Then, the converse of the relation becomes q -> p.
>>> Similarly, here p is AB = AC and q = 
>>> Hence, the converse becomes :
In a triangle ABC, if  then AB = AC.
then AB = AC.
Converse of “if in a triangle ABC, AB =AC then is In a triangle ABC, if
then AB = AC.
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
Ester gives nucleophilic addition reaction followed by elimination reaction with carbon nucleophile. When carbon nucleophile is of an ester then the reaction is known as Claisen condensation reaction. This reaction is also carried out between ester and a ketone. A successful Claisen condensation requires an ester with two a-hydrogens and an equivalent amount of base rather than a catalytic amount of base.
In the given reaction

Ester gives nucleophilic addition reaction followed by elimination reaction with carbon nucleophile. When carbon nucleophile is of an ester then the reaction is known as Claisen condensation reaction. This reaction is also carried out between ester and a ketone. A successful Claisen condensation requires an ester with two a-hydrogens and an equivalent amount of base rather than a catalytic amount of base.
In the given reaction

chemistry-General
chemistry-
Ester gives nucleophilic addition reaction followed by elimination reaction with carbon nucleophile. When carbon nucleophile is of an ester then the reaction is known as Claisen condensation reaction. This reaction is also carried out between ester and a ketone. A successful Claisen condensation requires an ester with two a-hydrogens and an equivalent amount of base rather than a catalytic amount of base.
In the given reaction :

Ester gives nucleophilic addition reaction followed by elimination reaction with carbon nucleophile. When carbon nucleophile is of an ester then the reaction is known as Claisen condensation reaction. This reaction is also carried out between ester and a ketone. A successful Claisen condensation requires an ester with two a-hydrogens and an equivalent amount of base rather than a catalytic amount of base.
In the given reaction :

chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which of the following compounds will be most easily hydrolysed ?
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which of the following compounds will be most easily hydrolysed ?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Acid derivatives although contain 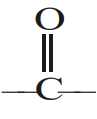 group, yet do not undergo the usual properties of carbonyl group It is due to:
group, yet do not undergo the usual properties of carbonyl group It is due to:
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Acid derivatives although contain 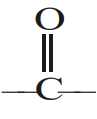 group, yet do not undergo the usual properties of carbonyl group It is due to:
group, yet do not undergo the usual properties of carbonyl group It is due to:
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which among the following ester is most reactive towards nucleophilic attack ?
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which among the following ester is most reactive towards nucleophilic attack ?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which of the most reactive acid derivative?
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which of the most reactive acid derivative?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which among the following anions is the most basic ?
The reactivity of acid derivatives in general follows the order :

The above order of reactivity can be explained in terms of the : (i) Basicity of leaving group (ii) Resonance effect (iii) Inductive effect Weaker is the basic character of leaving group, more is the reactivity of acid derivative. In general, all the acid derivatives show resonance as follows:

More is the stabilization, lesser is the reactivity and vice-versa.
Which among the following anions is the most basic ?
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1

Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1

Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1
Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



In the above reaction (P) and (Q) are respectively :
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1
Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



In the above reaction (P) and (Q) are respectively :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following compound give benzoic acid on KMnO4 oxidation
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following compound give benzoic acid on KMnO4 oxidation
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following statement is not correct
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following statement is not correct
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Compound z is :
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Compound z is :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.

In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.

chemistry-General
chemistry-
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.
Arrange the following amides according to their relative reactivity when reacted with Br2 in excess of strong base
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.
Arrange the following amides according to their relative reactivity when reacted with Br2 in excess of strong base
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
chemistry-General
physics-
The tube shown is of uniform cross–section. Liquid flows through it at a constant speed in the direction shown by the arrows. The liquid exerts on the tube

The tube shown is of uniform cross–section. Liquid flows through it at a constant speed in the direction shown by the arrows. The liquid exerts on the tube

physics-General



