Chemistry-
General
Easy
Question
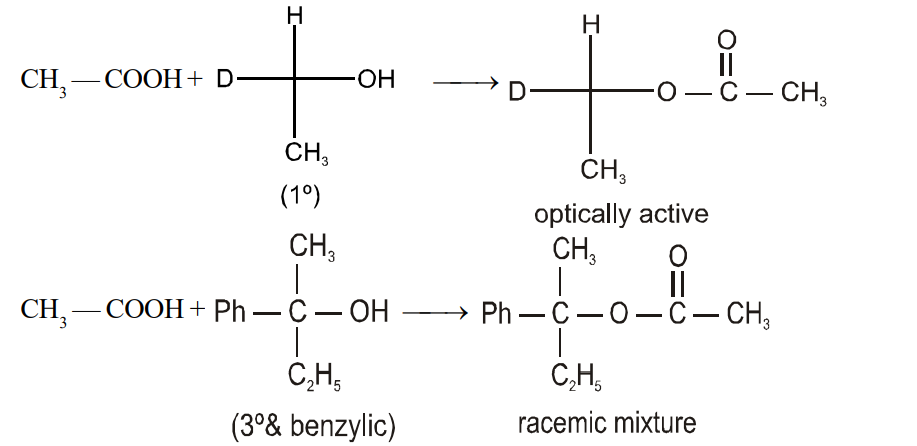
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1

Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



- (X) is optically active while (Y) is optically inactive
- Both (X) and (Y) are optically active
- Both (X) and (Y) are optically inactive
- (X) is optically inactive while (Y) is optically active
The correct answer is: (X) is optically active while (Y) is optically inactive
Related Questions to study
chemistry-
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1
Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



In the above reaction (P) and (Q) are respectively :
Observe the esterification mechanisms for primary and tertiary alcohols.
Type.1
Mechanism

Type. 2

Mechanism



In the above reaction (P) and (Q) are respectively :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following compound give benzoic acid on KMnO4 oxidation
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following compound give benzoic acid on KMnO4 oxidation
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following statement is not correct
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Which of the following statement is not correct
chemistry-General
chemistry-
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Compound z is :
Observe the following sequence of reaction and answer the questions based on it

Compound z is :
chemistry-General
chemistry-
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.

In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.

chemistry-General
chemistry-
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.
Arrange the following amides according to their relative reactivity when reacted with Br2 in excess of strong base
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
In the Hofmann rearrangement an unsubstituted amide is treated with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give a primary amine that has one carbon lesser than starting amide.
General reaction :

Mechanism :

If the migrating group is chiral then its configuration is retained. Electron releasing effects in the migrating group increases reactivity of Hofmann rearrangement.
Arrange the following amides according to their relative reactivity when reacted with Br2 in excess of strong base
I) 
II) 
III) 
IV) 
chemistry-General
physics-
The tube shown is of uniform cross–section. Liquid flows through it at a constant speed in the direction shown by the arrows. The liquid exerts on the tube

The tube shown is of uniform cross–section. Liquid flows through it at a constant speed in the direction shown by the arrows. The liquid exerts on the tube

physics-General
physics-
A bent arc shaped sealed glass tube filled with water is accelerated horizontally with acceleration a. A small air bubble inside it is found to be stuck at 1 cm from vertical axis. Neglect surface tension. What is the acceleration of the tube.

A bent arc shaped sealed glass tube filled with water is accelerated horizontally with acceleration a. A small air bubble inside it is found to be stuck at 1 cm from vertical axis. Neglect surface tension. What is the acceleration of the tube.

physics-General
physics-
A pan balance has a container of water with an overflow spout on the right-hand pan as shown. It is full of water right up to the overflow spout. A container on the left-hand pan is positioned to catch any water that overflows. The entire apparatus is adjusted so that it’s balanced. A brass weight on the end of a string is then lowered into the water, but not allowed to rest on the bottom of the container. What happens next?

A pan balance has a container of water with an overflow spout on the right-hand pan as shown. It is full of water right up to the overflow spout. A container on the left-hand pan is positioned to catch any water that overflows. The entire apparatus is adjusted so that it’s balanced. A brass weight on the end of a string is then lowered into the water, but not allowed to rest on the bottom of the container. What happens next?

physics-General
physics-
A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid which has mass density r. It is placed on a weigh-scale; the scale reading is W. A light ball which would float on the liquid if allowed to do so, of volume V and mass m is pushed gently down and held beneath the surface of the liquid with a rigid rod of negligible volume as shown on the left.

What is the reading of the scale when the ball is fully immersed?
A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid which has mass density r. It is placed on a weigh-scale; the scale reading is W. A light ball which would float on the liquid if allowed to do so, of volume V and mass m is pushed gently down and held beneath the surface of the liquid with a rigid rod of negligible volume as shown on the left.

What is the reading of the scale when the ball is fully immersed?
physics-General
physics-
A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid which has mass density r. It is placed on a weigh-scale; the scale reading is W. A light ball which would float on the liquid if allowed to do so, of volume V and mass m is pushed gently down and held beneath the surface of the liquid with a rigid rod of negligible volume as shown on the left.

What is the mass M of liquid which overflowed while the ball was being pushed into the liquid?
A cylindrical container of length L is full to the brim with a liquid which has mass density r. It is placed on a weigh-scale; the scale reading is W. A light ball which would float on the liquid if allowed to do so, of volume V and mass m is pushed gently down and held beneath the surface of the liquid with a rigid rod of negligible volume as shown on the left.

What is the mass M of liquid which overflowed while the ball was being pushed into the liquid?
physics-General
physics-
A cubical sealed vessel with edge L is placed on a cart, which is moving horizontally with an acceleration ‘a’ as shown in figure. The cube is filled with a ideal fluid having density r. The gauge pressure at the centre of the cubical vessel is

A cubical sealed vessel with edge L is placed on a cart, which is moving horizontally with an acceleration ‘a’ as shown in figure. The cube is filled with a ideal fluid having density r. The gauge pressure at the centre of the cubical vessel is

physics-General
physics-
The figure below shows four situations in which a gray liquid and a black liquid (which we known nothing about) are in a U tube.

In which of the following situation(s) of static equilibrium must the density of the gray liquid be greater than the density of the black liquid? (circle all appropriate cases)
The figure below shows four situations in which a gray liquid and a black liquid (which we known nothing about) are in a U tube.

In which of the following situation(s) of static equilibrium must the density of the gray liquid be greater than the density of the black liquid? (circle all appropriate cases)
physics-General
physics-
The figure below shows four situations in which a gray liquid and a black liquid (which we known nothing about) are in a U tube.

Which of the following situations does not show static equilibrium of liquids.
The figure below shows four situations in which a gray liquid and a black liquid (which we known nothing about) are in a U tube.

Which of the following situations does not show static equilibrium of liquids.
physics-General
physics-
An ideal monoatomic gas is carried around the cycle ABCDA as shown in the figure. The efficiency of the gas cycle is :

An ideal monoatomic gas is carried around the cycle ABCDA as shown in the figure. The efficiency of the gas cycle is :

physics-General