Maths-
General
Easy
Question
Tangents are drawn to the ellipse  at the ends of the latus rectum. The are of the quadrilateral so formed is
at the ends of the latus rectum. The are of the quadrilateral so formed is
- 27


- 45

The eccentricity of an ellipse is always less than 1. i.e. e < 1. The eccentricity of an ellipse can be taken as the ratio of its distance from the focus and the distance from the directrix.
Eccentricity of ellipse (e) = 
Here a is the length of the semi-major axis and b is the length of the semi-minor axis.
The correct answer is: 27
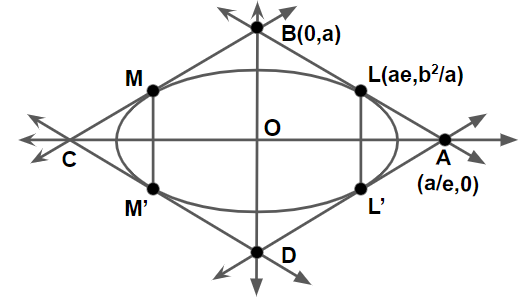
Let LL′ and MM′ are the latus rectum.
Eccentricity of ellipse (e) = 
Here a is the length of the semi-major axis and b is the length of the semi-minor axis.

The equation of tangent at (x1,y1) is 
The tangent passes through point L (ae, 
, 
So, the tangent cuts the x-axis at point A(a/e,0) and y-axis at point B(0,a)
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 4×area of △OAB
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 27sq. units
Related Questions to study
Maths-
A tangent to the ellipse x2 + 4y2 = 4 meets the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 at P and Q. The angle between the tangents at P and Q of the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 is
A tangent to the ellipse x2 + 4y2 = 4 meets the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 at P and Q. The angle between the tangents at P and Q of the ellipse x2 + 2y2 = 6 is
Maths-General
physics
Here are the graphs of x→ t of moving body. which of them is not suitable?
Here are the graphs of x→ t of moving body. which of them is not suitable?
physicsGeneral
Maths-
A cubic polynomial f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d has a graph which touches the x-axis at 2, has another x-intercept at –1 and has y-intercept at –2 as shown. The value of, a + b + c + d equals

A cubic polynomial f(x) = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d has a graph which touches the x-axis at 2, has another x-intercept at –1 and has y-intercept at –2 as shown. The value of, a + b + c + d equals

Maths-General
Maths-
Consider f(x) = |1–x| 1 £ x £ 2 and g(x )= f(x) + b  , 1 £ x £ 2 then which of the following is correct?
, 1 £ x £ 2 then which of the following is correct?
Consider f(x) = |1–x| 1 £ x £ 2 and g(x )= f(x) + b  , 1 £ x £ 2 then which of the following is correct?
, 1 £ x £ 2 then which of the following is correct?
Maths-General
Maths-
The value of c in Lagrange’s theorem for the function f(x) = log sin x in the interval  is -
is -
The value of c in Lagrange’s theorem for the function f(x) = log sin x in the interval  is -
is -
Maths-General
physics
The relation between time and displacement of a moving particle is given by  where
where  is a constant. The shape of the graph is
is a constant. The shape of the graph is  is....
is....
The relation between time and displacement of a moving particle is given by  where
where  is a constant. The shape of the graph is
is a constant. The shape of the graph is  is....
is....
physicsGeneral
Maths-
If P (q) and Q  are two points on the ellipse
are two points on the ellipse  , then locus of the mid – point of PQ is
, then locus of the mid – point of PQ is
If P (q) and Q  are two points on the ellipse
are two points on the ellipse  , then locus of the mid – point of PQ is
, then locus of the mid – point of PQ is
Maths-General
Maths-
If CP and CD are semi – conjugate diameters of an ellipse  then CP2 + CD2 =
then CP2 + CD2 =
If CP and CD are semi – conjugate diameters of an ellipse  then CP2 + CD2 =
then CP2 + CD2 =
Maths-General
Maths-
The normals to the curve x = a ( + sin
+ sin  ), y = a (1 – cos
), y = a (1 – cos  ) at the points
) at the points  = (2n + 1)
= (2n + 1)  , n
, n  I are all -
I are all -
The normals to the curve x = a ( + sin
+ sin  ), y = a (1 – cos
), y = a (1 – cos  ) at the points
) at the points  = (2n + 1)
= (2n + 1)  , n
, n  I are all -
I are all -
Maths-General
Maths-
The normal to the curve x = 3 cos  –
–  , y = 3 sin
, y = 3 sin  –
– 
 at the point
at the point  =
=  /4 passes through the point -
/4 passes through the point -
The normal to the curve x = 3 cos  –
–  , y = 3 sin
, y = 3 sin  –
– 
 at the point
at the point  =
=  /4 passes through the point -
/4 passes through the point -
Maths-General
Maths-
The normal of the curve given by the equation x = a (sin + cos
+ cos ), y = a (sin
), y = a (sin – cos
– cos ) at the point Q is -
) at the point Q is -
The normal of the curve given by the equation x = a (sin + cos
+ cos ), y = a (sin
), y = a (sin – cos
– cos ) at the point Q is -
) at the point Q is -
Maths-General
Maths-
If the tangent at ‘t’ on the curve y =  , x =
, x =  meets the curve again at
meets the curve again at  and is normal to the curve at that point, then value of t must be -
and is normal to the curve at that point, then value of t must be -
If the tangent at ‘t’ on the curve y =  , x =
, x =  meets the curve again at
meets the curve again at  and is normal to the curve at that point, then value of t must be -
and is normal to the curve at that point, then value of t must be -
Maths-General
Maths-
The tangent at ( ,
,  –
–  ) on the curve y =
) on the curve y =  –
–  meets the curve again at Q, then abscissa of Q must be -
meets the curve again at Q, then abscissa of Q must be -
The tangent at ( ,
,  –
–  ) on the curve y =
) on the curve y =  –
–  meets the curve again at Q, then abscissa of Q must be -
meets the curve again at Q, then abscissa of Q must be -
Maths-General
Maths-
If  = 1 is a tangent to the curve x = 4t,y =
= 1 is a tangent to the curve x = 4t,y = , t
, t  R then -
R then -
If  = 1 is a tangent to the curve x = 4t,y =
= 1 is a tangent to the curve x = 4t,y = , t
, t  R then -
R then -
Maths-General
Maths-
The line  +
+  = 1 touches the curve
= 1 touches the curve  at the point :
at the point :
The line  +
+  = 1 touches the curve
= 1 touches the curve  at the point :
at the point :
Maths-General



