Physics-
General
Easy
Question
A particle of mass  moves in the
moves in the  plane with a velocity
plane with a velocity  along the straight line
along the straight line  . If the angular momentum of the particle with respect to origin
. If the angular momentum of the particle with respect to origin  is
is  when it is at
when it is at  and
and  when it is at
when it is at  , then
, then



- The relationship between
 and
and  depends upon the slope of the line
depends upon the slope of the line 

The correct answer is: 
From the definition of angular momentum,
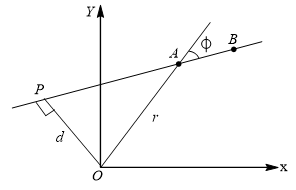

Therefore, the magnitude of  is
is

where  is the distance of closest approach of the particle to the origin. As
is the distance of closest approach of the particle to the origin. As  is same for both the particles, hence
is same for both the particles, hence  .
.
Related Questions to study
maths-
Assertion (A): If the system of equations  have non zero solution then
have non zero solution then 
Reason (R): If the system of equations  has a non zero solution then
has a non zero solution then  is singular
is singular
Assertion (A): If the system of equations  have non zero solution then
have non zero solution then 
Reason (R): If the system of equations  has a non zero solution then
has a non zero solution then  is singular
is singular
maths-General
physics-
Consider a body, shown in figure, consisting of two identical balls, each of mass  connected by a light rigid rod. If an impulse
connected by a light rigid rod. If an impulse is impared to the body at one of its ends, what would be its angular velocity?
is impared to the body at one of its ends, what would be its angular velocity?

Consider a body, shown in figure, consisting of two identical balls, each of mass  connected by a light rigid rod. If an impulse
connected by a light rigid rod. If an impulse is impared to the body at one of its ends, what would be its angular velocity?
is impared to the body at one of its ends, what would be its angular velocity?

physics-General
physics-
A binary star consists of two stars  (mass 2.2
(mass 2.2  ) and B (mass 11
) and B (mass 11  ), where
), where  is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance
is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance  and are rotating about their centre of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star
and are rotating about their centre of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star  about the centre of mass is
about the centre of mass is
A binary star consists of two stars  (mass 2.2
(mass 2.2  ) and B (mass 11
) and B (mass 11  ), where
), where  is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance
is the mass of the sun. They are separated by distance  and are rotating about their centre of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star
and are rotating about their centre of mass, which is stationary. The ratio of the total angular momentum of the binary star to the angular momentum of star  about the centre of mass is
about the centre of mass is
physics-General
physics-
A force of- F  acts on
acts on  , the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point 1, -(a) is
, the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point 1, -(a) is

A force of- F  acts on
acts on  , the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point 1, -(a) is
, the origin of the coordinate system. The torque about the point 1, -(a) is

physics-General
Maths-
The area of the region bounded by y=|x-1| and y=1 in sq. units is

For such questions, we should know area of different shapes.
The area of the region bounded by y=|x-1| and y=1 in sq. units is

Maths-General
For such questions, we should know area of different shapes.
Maths-
The area of the elliptic quadratic with the semi major axis and semi minor axis as 6 and 4 respectively

For such questions, we should know the formula of area of different shapes.
The area of the elliptic quadratic with the semi major axis and semi minor axis as 6 and 4 respectively

Maths-General
For such questions, we should know the formula of area of different shapes.
physics-
A solid sphere of radius  has moment of inertia
has moment of inertia  about its geometrical axis. If it is melted into a disc of radius
about its geometrical axis. If it is melted into a disc of radius  and thickness
and thickness  . If its moment of inertia about the tangential axis (which is perpendicular to plane of the disc), is also equal to
. If its moment of inertia about the tangential axis (which is perpendicular to plane of the disc), is also equal to  , then the value of
, then the value of  is equal to
is equal to

A solid sphere of radius  has moment of inertia
has moment of inertia  about its geometrical axis. If it is melted into a disc of radius
about its geometrical axis. If it is melted into a disc of radius  and thickness
and thickness  . If its moment of inertia about the tangential axis (which is perpendicular to plane of the disc), is also equal to
. If its moment of inertia about the tangential axis (which is perpendicular to plane of the disc), is also equal to  , then the value of
, then the value of  is equal to
is equal to

physics-General
Maths-
The area of the region bounded by y= and the x-axis is
and the x-axis is

The area of the region bounded by y= and the x-axis is
and the x-axis is

Maths-General
Maths-
Area of the region bounded by y is
is

Area of the region bounded by y is
is

Maths-General
Maths-
Area of the region bounded by y= and y=2 is
and y=2 is

Area of the region bounded by y= and y=2 is
and y=2 is

Maths-General
Maths-
The area bounded by y=cos x, y=x+1 and y=0 in the second quadrant is

The area bounded by y=cos x, y=x+1 and y=0 in the second quadrant is

Maths-General
physics-
A  joint is formed by two identical rods
joint is formed by two identical rods  and
and  each of mass
each of mass  and length
and length  in the
in the  plane as shown. Its moment of inertia about axis coinciding with
plane as shown. Its moment of inertia about axis coinciding with  is
is

A  joint is formed by two identical rods
joint is formed by two identical rods  and
and  each of mass
each of mass  and length
and length  in the
in the  plane as shown. Its moment of inertia about axis coinciding with
plane as shown. Its moment of inertia about axis coinciding with  is
is

physics-General
Maths-
The area bounded by the parabola =4ay, x-axis and the straight-line y=2a is
=4ay, x-axis and the straight-line y=2a is
The area bounded by the parabola =4ay, x-axis and the straight-line y=2a is
=4ay, x-axis and the straight-line y=2a is
Maths-General
physics-
Four balls each of radius 10 cm and mass 1 kg, 2kg, 3 kg and 4 kg are attached to the periphery of massless plate of radius 1 m. What is moment of inertia of the system about the centre of plate?

Four balls each of radius 10 cm and mass 1 kg, 2kg, 3 kg and 4 kg are attached to the periphery of massless plate of radius 1 m. What is moment of inertia of the system about the centre of plate?

physics-General
physics-
For the given uniform square lamina  , whose centre is
, whose centre is 

For the given uniform square lamina  , whose centre is
, whose centre is 

physics-General



